@GetMapping("/pathVariable2/{id}")
public String pathVariable2(@PathVariable(value = "id")
String id){
return id;
}调用:http://localhost:8082/pathVariable2/2
@GetMapping("/requestParam")
public String requestParam(String userName,String age){
return userName+":xxx:"+age;
}1)http://localhost:8082/requestParam 返回 null:xxx:null
2)http://localhost:8082/requestParam?userName=zhangsan 返回 zhangsan:xxx:null
3)http://localhost:8082/requestParam?userName=zhangsan&age=11 返回 zhangsan:xxx:11
以上说明,参数可传可不传
@PostMapping("/requestParamPost")
public String requestParamPost(String userName,String age){
return userName+":xxx:"+age;
}(注意是postman的post请求调用)post请求:http://localhost:8082/requestParam?userName=zhangsan&age=11 对比发现,如果是字符串参数,get post请求效果一样
@GetMapping("/requestParam2")
public String requestParam2(@RequestParam("uname") String userName,
@RequestParam String age){
return userName+":xxx:"+age;
}http://localhost:8082/requestParam2?uname=zhangsan&age=11
@PostMapping("/requestParam2")
public String requestParam2(@RequestParam("uname") String userName,
@RequestParam String age){
return userName+":xxx:"+age;
}(注意是postman的post请求调用)post请求:http://localhost:8082/requestParam2?uname=zhangsan&age=11
它就不能支持get请求了,所以这里只有post请求,注意:只支持单个参数
@PostMapping("/RequestBody2")
public String requestBody2(@RequestBody String name){
return "name is:"+name;
}
@GetMapping("/requestParam3")
public String requestParam3(User user){
return user.getId()+":xxx:"+user.getName();
}http://localhost:8082/requestParam3?name=zhangsan&id=11
@PostMapping("/requestParam4")
public String requestParam4(User user){
return user.getId()+":xxx:"+user.getName();
}(注意是postman的post请求调用)http://localhost:8082/requestParam4?name=zhangsan&id=11
除了请求方式外和get是一样的,同时传递字符串参数和对象也是一样的
注意:请不要这么做,要么不加注解,要么用下面的方式
老规矩,还是只支持post请求
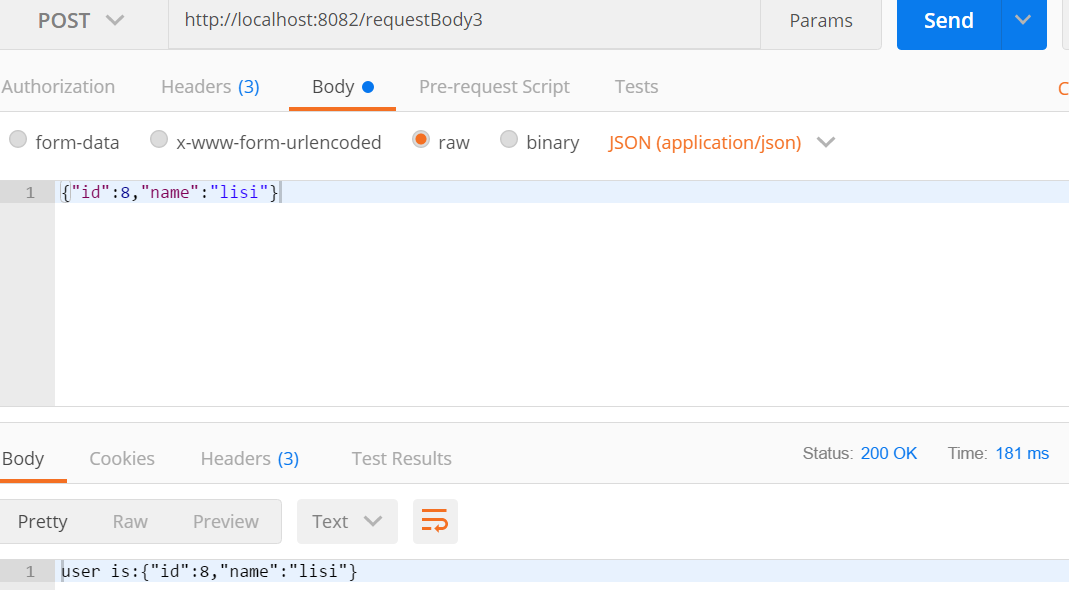
@PostMapping("/requestBody3")
public String requestBody3(@RequestBody User user){
return "user is:"+ JSON.toJSONString(user);
}
@GetMapping("/requestParam5")
public String requestParam5(String[] aa){
return JSON.toJSONString(aa);
}http://localhost:8082/requestParam5?aa=1&aa=2
@PostMapping("/requestParam6")
public String requestParam6(String[] aa){
return JSON.toJSONString(aa);
}(postman调用post方式) http://localhost:8082/requestParam6?aa=1&aa=2
方式和效果跟上面完全一样,同时字符串的传递,加不加@RequestParam的效果和做法都一样,加了就多了必传的效果
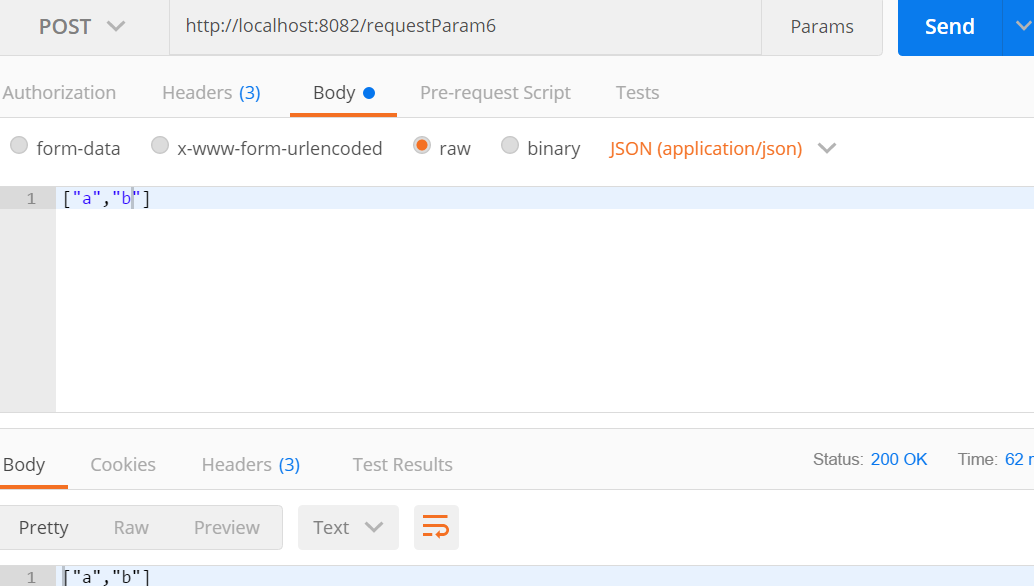
@PostMapping("/requestParam6")
public String requestParam6(@RequestBody String[] aa){
return JSON.toJSONString(aa);
}
推荐使用@RequestBody
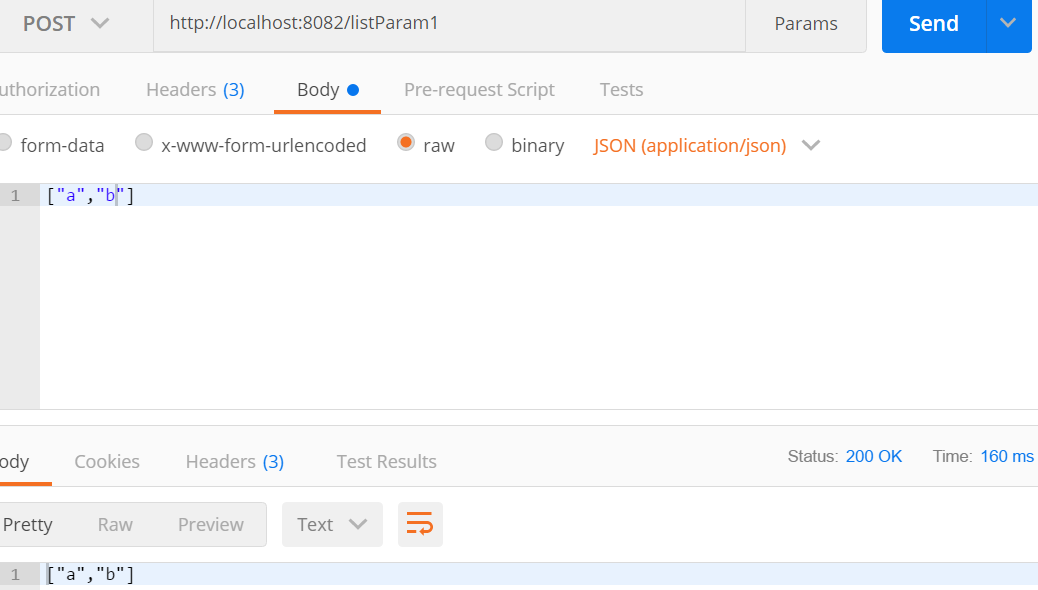
@PostMapping("/listParam1")
public String listParam1(@RequestBody List<String> aa){
return JSON.toJSONString(aa);
}
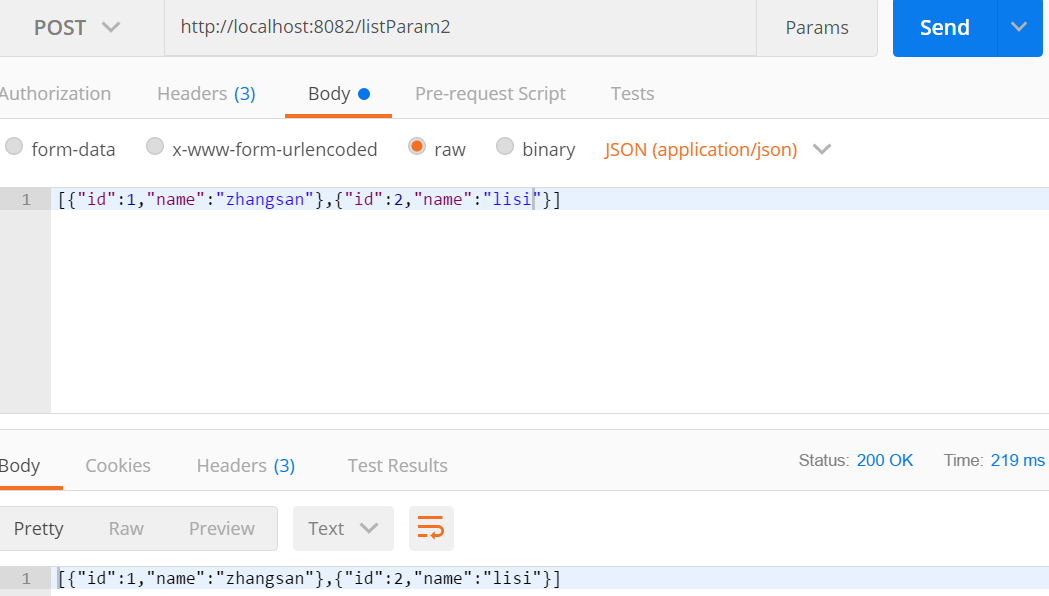
@PostMapping("/listParam2")
public String listParam2(@RequestBody List<User> aa){
return JSON.toJSONString(aa);
}
这里说下,map和对象其实本质是一样的
@PostMapping("/mapParam1")
public String mapParam1(@RequestBody Map<String,String> map){
return JSON.toJSONString(map);
}
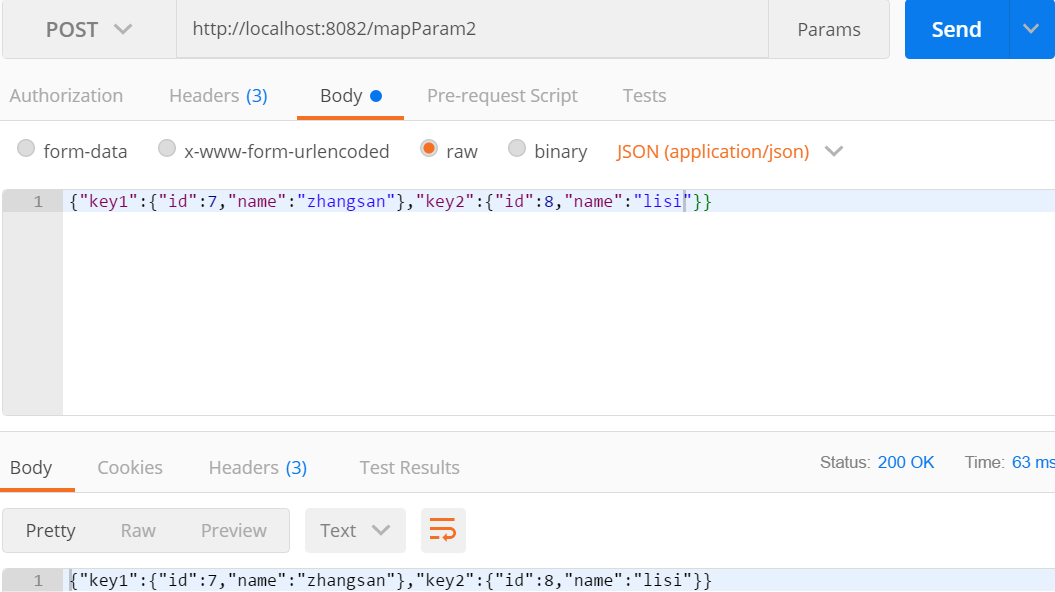
@PostMapping("/mapParam2")
public String mapParam2(@RequestBody Map<String,User> map){
return JSON.toJSONString(map);
}
扩展:https://blog.csdn.net/a654540233/article/details/84936908