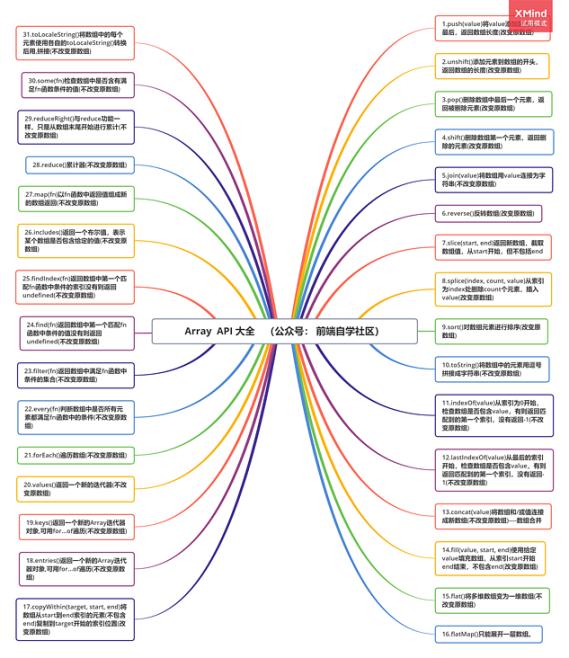
我们在日常开发中,与接口打交道最多了,前端通过访问后端接口,然后将接口数据二次处理渲染到页面当中。
二次处理的过程是 考验 Coder 对 Array 是否熟练 以及 在 何种 场景下使用哪种方法处理最优 。
小编,在最近开发中就遇到了 Array 问题, 在处理复杂的业务需求时,没想到Array 有类似的方法,然后将方法 组合起来解决当下问题。
forEach()forEach() 方法按照升序为数组中每一项执行一次给定的函数。
语法
arr.forEach(callback(currentValue , index , array) ,thisArg)
currentValue : 数组当前项值index : 数组当前项索引arr : 数组对象本身thisArg : 可选参数。当执行回调函数 callback 时,用作 this 的值。注意
thisArg 参数会被忽略,因为箭头函数在词法上绑定了 this 值。forEach 不会直接改变调用它的对象,但是那个对象可能会被 callback 函数改变。every 不会改变原数组。//防盗贴:微信公众号: 前端自学社区
const arr = [2,3,4,1,44]
arr.forEach(val =>{
console.log(`值为${val*2}`)
})
console.log(`原数组为${arr}`);
// 值为4
// 值为6
// 值为8
// 值为2
// 值为88
// 原数组为2,3,4,1,44reduce()reduce()数组元素累计器,返回一个合并的结果值。
语法
arr.reduce(callback(accumulator, currentValue, index, array), initialValue)
accumulator : 累计器,默认为数组元素第一个值currentValue : 当前值index : 当前元素索引 <font>可选</font>array : 数组 <font>可选</font>initialValue : 初始值 <font>可选</font>reduce 有两个参数,一个是回调函数,一个是初始值。
它有两种取值情况:
initialValue 初始值时, 那么accumulator 的值为 initialValue , currentValue 的值为 数组第一个值initialValue 初始值时, 那么 accumulator 的值 为 数组第一个值, currentValue 为第二个值。注意
initialValue 初始值时,会抛出 TypeError .initialValue 或者 提供了initialValue ,数组为空,那么唯一值被返回不会执行 callback 回调函数。求和
//防盗贴:微信公众号: 前端自学社区/ const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4] const sum = arr.reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue, 10) console.log(sum) //20 // accumulator 累计器 // currentValue 当前值 // initialValue 累计 初始值 为10 //10 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 ## 注意 // 回调函数第一次执行时,accumulator 和currentValue的取值有两种情况: // 如果调用reduce()时提供了initialValue,accumulator取值为initialValue,currentValue取数组中的第一个值; // 如果没有提供 initialValue,那么accumulator取数组中的第一个值,currentValue取数组中的第二个值。
计算对象中的值
要累加对象数组中包含的值,必须提供初始值,以便各个item正确通过你的函数。
/*
* @Description:
* @Author: 微信公众号: 前端自学社区
* @Date: 2021-08-07 00:53:51
* @LastEditTime: 2021-08-07 00:53:51
* @LastEditors: Do not edit
*/
const data = [
{
date: '2021-8-1',
income: 200
},
{
date: '2021-8-2',
income: 400
},
{
date: '2021-8-3',
income: 300
},
]
console.log(`总收入: ${data.reduce( (pre,currentValue) => pre + currentValue.income,0)}`);
//总收入: 900二维数组转一位数组
const array = [[1,2],[3,4]] console.log(array.reduce((a,b) => a.concat(b))); //[ 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
find()find() 返回满足特定条件的元素对象或者元素值, 不满足返回 undefined
语法
arr.find((element,index,array), thisArg)
element : 当前元素index : 当前元素索引 <font>可选</font>array : 数组本身 <font>可选</font>thisArg : 执行回调时用作this 的对象。 <font>可选</font>// 从数据中找出第一个满足特定条件的对象
const data = [
{
name:'张三',
article: 3
},
{
name:'老王',
article: 9
},
{
name:'老李',
article: 10
}
]
console.log(data.find(item => item.article > 9 ));
// { name: '老李', article: 10 }findIndex()findIndex() 返回数组中符合条件的第一个元素的索引,没有,则返回 -1 。
语法
arr.findIndex((element,index,array), thisArg)
element : 当前元素index : 当前元素索引 <font>可选</font>array : 数组本身 <font>可选</font>thisArg : 执行回调时用作this 的对象。 <font>可选</font>const arr = [22,33,44,55] console.log(arr.findIndex(val => val > 33)); //2 console.log(arr.findIndex(val => val > 99)); //-1
key()key() 返回一个新的Array Iterator对象,该对象包含数组中每个索引的键。
语法
keys()
注意
const inputModal = [
{
name:''
},
{
age:''
},
{
hobby:''
}
]
for(const key of inputModal.keys()){
console.log(key)
}
// 0
// 1
// 2
const arr = [1,2,,3]
for(const key of arr.keys()){
console.log(key);
}
// 0
// 1
// 2
// 3
//Object.keys() 方法会返回一个由一个给定对象的自身可枚举属性组成的数组
// 所以 Object.keys(arr) = [ '0', '1', '3' ]
for(const key of Object.keys(arr)){
console.log(key);
}
// 0
// 1
// 3
values()values() 方法返回一个新的 Array Iterator 对象,该对象包含数组每个索引的值。
语法
arr.values()
const Color = ['red','yelloe','orange']
for(val of Color.values()){
console.log(val);
}
// red
// yelloe
// orange
<hr/>
every()every 用来判断数组内所有元素是否符合某个条件,返回 布尔值
语法
arr.every(callback(currentValue , index , array) ,thisArg)
currentValue : 数组当前项值 <font>必须</font>index : 数组当前项索引 <font>可选</font>arr : 数组对象本身<font>可选</font>thisArg : 可选参数。当执行回调函数 callback 时,用作 this 的值。<font>可选</font>注意
trueevery 不会改变原数组。true。//防盗贴:微信公众号: 前端自学社区
const arr = [2,3,4,1,44]
console.log(arr.every(val => val > 0 )); //true
console.log(arr.every(val => { val > 2 })) //false
some()some() 用来判断数组元素是否符合某个条件,只要有一个元素符合,那么返回 true.
语法
arr.some(callback(currentValue , index , array) ,thisArg)
currentValue : 数组当前项值 <font>必须</font>index : 数组当前项索引 <font>可选</font>arr : 数组对象本身<font>可选</font>thisArg : 可选参数。当执行回调函数 callback 时,用作 this 的值。<font>可选</font>注意
some() 被调用时不会改变数组。false。some() 在遍历时,元素范围已经确定,在遍历过程中添加的元素,不会加入到遍历的序列中。const arr = [2,3,4,1,44]
console.log(arr.some(val => val > 2)) //true
console.log([].some(val => val > 2 )); //false
const newList = [11,22,33,44]
console.log(newList.some(val => {
newList.push(55)
newList.push(66)
val > 55
})); //false
filter()filter() 用来遍历原数组,过滤拿到符合条件的数组元素,形成新的数组元素。
语法
arr.some(callback(currentValue , index , array) ,thisArg)
currentValue : 数组当前项值 <font>必须</font>index : 数组当前项索引 <font>可选</font>arr : 数组对象本身<font>可选</font>thisArg : 可选参数。当执行回调函数 callback 时,用作 this 的值。<font>可选</font>注意
filter 不会改变原数组,它返回过滤后的新数组。filter() 在遍历时,元素范围已经确定,在遍历过程中添加的元素,不会加入到遍历的序列中。const arr = [11,22,33,44,55,66]
console.log(arr.filter(val => val > 44 ))
console.log(`原数组为${arr}`);
// [ 55, 66 ]
// 原数组为11,22,33,44,55,66
map()map() 创建一个新的数组,其结果是该数组中的每个元素都调用一个提供的函数后返回的结果。
语法
arr.map(callback(currentValue , index , array) ,thisArg)
currentValue : 数组当前项值 <font>必须</font>index : 数组当前项索引 <font>可选</font>arr : 数组对象本身<font>可选</font>thisArg : 可选参数。当执行回调函数 callback 时,用作 this 的值。<font>可选</font>注意
map 不修改调用它的原数组本身map() 在遍历时,元素范围已经确定,在遍历过程中添加的元素,不会加入到遍历的序列中。const arr = [1,2,3,4] console.log(arr.map(val => val*3 )) // [ 3, 6, 9, 12 ] console.log(arr) // [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
<hr/>
reverse()reverse() 方法将数组中元素的位置颠倒,并返回该数组。数组的第一个元素会变成最后一个,数组的最后一个元素变成第一个。该方法会改变原数组。
const arr = [1,2,3] console.log(arr.reverse(11,22,33)) //[ 3, 2, 1 ]
sort()sort() 方法采用 原地算法进行排序并返回数组。默认排序顺序是在将元素转换为字符串,然后比较它们的UTF-16代码单元值序列
原地算法是一个使用辅助的数据结构对输入进行转换的算法。但是,它允许有少量额外的存储空间来储存辅助变量。当算法运行时,输入通常会被输出覆盖。原地算法仅通过替换或交换元素来更新输入序列。
const arr = [23,11,33,44,1] console.log(arr.sort()) //[ 1, 11, 23, 33, 44 ] const arr = [23,11,33,44,1000000000] console.log(arr.sort()) // [ 1000000000, 11, 23, 33, 44 ]
shift()shift() 方法从数组中删除第一个元素,并返回该元素的值。此方法更改数组的长度。
语法
arr.shift()
注意
undefinedconst data = [
{
id:1,
name:'前端'
},
{
id:2,
name:'后端'
},
{
id:3,
name:'移动端'
},
{
id:4,
name:'嵌入式开发'
},
]
const deleObj = data.shift()
console.log('==============删除后的元素======================');
console.log(data);
console.log('=================删除后的元素===================');
console.log('===============被删除的元素=====================');
console.log(deleObj);
console.log('================被删除的元素====================');
// ==============删除后的元素======================
// [
// { id: 2, name: '后端' },
// { id: 3, name: '移动端' },
// { id: 4, name: '嵌入式开发' }
// ]
// =================删除后的元素===================
// ===============被删除的元素=====================
// { id: 1, name: '前端' }
// ================被删除的元素====================
pop()pop()方法从数组中删除最后一个元素,并返回该元素的值。此方法更改数组的长度。
用法和 shift 类似。
语法
arr.pop()
注意
undefinedconst data = [
{
id:1,
name:'前端'
},
{
id:2,
name:'后端'
},
{
id:3,
name:'移动端'
},
{
id:4,
name:'嵌入式开发'
},
]
const deleObj = data.pop()
console.log(data);
// [
// { id: 1, name: '前端' },
// { id: 2, name: '后端' },
// { id: 3, name: '移动端' }
// ]
console.log(deleObj);
// { id: 4, name: '嵌入式开发' }
splice()splice() 方法通过删除或替换现有元素或者原地添加新的元素来修改数组,并以数组形式返回被修改的内容。此方法会改变原数组。
语法
array.splice(start,deleteCount, [item1,item2....])
start : 开始的索引deleteCount : 删除的个数 <font>可选</font>[item1,item2 .....] ;从开始的索引进行 添加的增加和替换的元素, <font>可选</font>注意
如果只传递了开始的索引位置,则会删除索引后的所有元素对象
const data = [
{
id:1,
name:'前端'
},
{
id:2,
name:'后端'
},
{
id:3,
name:'移动端'
},
{
id:4,
name:'嵌入式开发'
},
]
data.splice(1)
console.log(data)
// [ { id: 1, name: '前端' } ]
从索引为 2 开始, 删除 1 个数组元素对象,添加两个数组元素对象
const data = [
{
id:1,
name:'前端'
},
{
id:2,
name:'后端'
},
{
id:3,
name:'移动端'
},
{
id:4,
name:'嵌入式开发'
},
]
data.splice(2,1,...[{id:5,name:'人工智能'},{id:6,name:'大数据开发'}])
console.log(data);
// [
// { id: 1, name: '前端' },
// { id: 2, name: '后端' },
// { id: 5, name: '人工智能' },
// { id: 6, name: '大数据开发' },
// { id: 4, name: '嵌入式开发' }
// ]
splice()上面已经有介绍
push()push() 方法将一个或多个元素添加到数组的末尾,并返回该数组的新长度。
语法
arr.push(element1, ..., elementN)
const data = [
{
id:1,
name:'前端'
},
{
id:2,
name:'后端'
},
]
console.log(data.push({id:3,name:'移动端'})) //3
合并数组
const data = [
{
id:1,
name:'前端'
},
{
id:2,
name:'后端'
},
]
var obj = [
{
id:4,
name:'嵌入式开发'
},
]
// 相当于 data.push({id:4,name:'嵌入式开发'});
Array.prototype.push.apply(data, obj);
console.log(data);
[
{ id: 1, name: '前端' },
{ id: 2, name: '后端' },
{ id: 4, name: '嵌入式开发' }
]
unshift()unshift() 方法将一个或多个元素添加到数组的开头,并返回该数组的新长度。
const arr = [1,2,3] console.log(arr.unshift(11,22,33)) //6 console.log(arr) //[ 11, 22, 33, 1, 2, 3 ]
indexOf()indexOf()方法返回可以在数组中找到给定元素的第一个索引,如果不存在,则返回 -1。
语法
indexOf(searchElement) indexOf(searchElement, fromIndex)
searchElement : 要查找的元素fromIndex : 按指定的索引进行查找出现的指定元素的第一个索引。 <font>可选</font>
const arr = [1,1,2,3,4,5,4,4,6] console.log(arr.indexOf(3)); //3 console.log(arr.indexOf(9)); //-1 console.log(arr.indexOf(3,4)); //-1 //从索引为 4 的元素进行查找 3, 显然后面没有3 , 返回 -1
数组去重
创建一个新的空数组,通过indexOf 来判断空数组是否第一次存在某个元素,
push 到空数组中.const newArr = []
arr.forEach(val => {
if(newArr.indexOf(val) < 0){
newArr.push(val)
}
})
console.log(newArr);
// [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ]
lastIndexOf()lastIndexOf() 查找数组中元素最后一次出现的索引,如未找到返回-1。
如果不存在则返回 -1。从数组的后面向前查找,从 fromIndex 处开始。
语法
arr.lastIndexOf(searchElement, fromIndex)
searchElement : 要查找的元素fromIndex : 按指定的索引进行查找出现的指定元素的第一个索引。 <font>可选</font>
arr.length - 1),即整个数组都被查找。注意
lastIndexOf 使用的是 严格相等 === 比较 searchElement 和数组中的元素。const arr = [1,1,2,3,4,5,4,4,6] console.log(arr.lastIndexOf(4)); //7 console.log(arr.lastIndexOf(4,11)); //7 指定的查找的索引 大于 数组的长度, 会进行整个数组查找 console.log(arr.lastIndexOf(4,-33)); // -1 指定的索引为负数,且绝对值大于数组长度, 则返回 -1 console.log(arr.lastIndexOf(4,-5)); //4 指定的索引为负数,且绝对值小于数组长度, 则会 从向前进行查找
inCludes()includes() 方法用来判断一个数组是否包含一个指定的值,根据情况,如果包含则返回 true,否则返回false。
语法
arr.includes(searchElement, fromIndex)
searchElement : 要查找的元素
查找时,区分大小写
fromIndex : 按指定的索引进行查找出现的指定元素的第一个索引。 <font>可选</font>
array.length + fromIndex 的索引开始搜fromIndex 大于等于数组的长度,则会返回 false,且该数组不会被搜索。const arr = [1,1,2,3,4,5,4,4,6] console.log(arr.includes(4)); //true console.log(arr.includes(4,66)); //false console.log(arr.includes(1,-1)); //false
concat()concat() 方法用于合并两个或多个数组。
语法
var new_array = old_array.concat([arr1][arr2])
注意
concat方法不会改变this或任何作为参数提供的数组,而是返回一个浅拷贝,它包含与原始数组相结合的相同元素的副本
- 对象引用(而不是实际对象):
concat将对象引用复制到新数组中。 原始数组和新数组都引用相同的对象。 也就是说,如果引用的对象被修改,则更改对于新数组和原始数组都是可见的。 这包括也是数组的数组参数的元素。- 数据类型如字符串,数字和布尔(不是
String,Number和Boolean) 对象):concat将字符串和数字的值复制到新数组中。
let arr1 = [1,2,3]
let arr2 = [4,5,6]
let arr3 = [[1,2],[3,4]]
console.log(arr1.concat(arr2));
//[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ]
// 嵌套合并
console.log(arr1.concat(arr2).concat(arr3));
// [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, [ 1, 2 ], [ 3, 4 ] ]
let obj1 = [{a:1},{b:2}]
let obj2 = [{c:3},{d:4}]
let obj3 = obj1.concat(obj2)
console.log(obj3);
//[ { a: 1 }, { b: 2 }, { c: 3 }, { d: 4 } ]
obj1[0].a = 4 //改变obj[0]对象值,会直接影响合并后的数组,因为是浅拷贝
console.log(obj3);
//[ { a: 4 }, { b: 2 }, { c: 3 }, { d: 4 } ]
toString()toString() 返回一个字符串,表示指定的数组及其元素。
当一个数组被作为文本值或者进行字符串连接操作时,将会自动调用其 toString 方法。
对于数组对象,toString 方法连接数组并返回一个字符串,其中包含用逗号分隔的每个数组元素。
语法
arr.toString()
const arr = [1,2,3] console.log(arr.toString()); //1,2,3
join()join()方法通过连接数组元素用逗号或指定的分隔符字符串分隔,返回一个字符串。
如果数组只有一项,则将在不使用分隔符的情况下返回该项。
语法
join() join(separator)
separator : 指定的分割的 字符 <font>可选</font>const arr = ['2021','08','08']
console.log(arr.join()); //2021,08,08
console.log(arr.join('-')); //2021-08-08
console.log(arr.join('/')); //2021/08/08
slice()slice() 方法返回一个新的数组对象,这一对象是一个由 begin 和 end 决定的原数组的浅拷贝(包括 begin,不包括end)。原始数组不会被改变。
语法
arr.slice(begin, end)
begin : 指定截取的开始索引 <font>可选</font>
- 默认从0 开始
- 如果
begin为负数,则以数组末尾开始 的 绝对值开始截取slice(-2)末尾第2个元素- 如果
begin超出原数组的索引范围,则会返回空数组。
end : 指定截取的结束索引 <font>可选</font>
- 如果
end被省略,则slice会一直提取到原数组末尾。- 如果
end大于数组的长度,slice也会一直提取到原数组末尾。- 如果
end为负数, 则它表示在原数组中的倒数第几个元素结束抽取。
const arr = [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88] console.log(arr.slice(1,4)); // 应该返回 索引 1 - 3 的数组元素 // [ 22, 33, 44 ] console.log(arr.slice(-4,2)) //[] console.log(arr.slice(-4)); //[ 55, 66, 77, 88 ] console.log(arr.slice(0,-1)); // [ // 11, 22, 33, 44, // 55, 66, 77 // ]